Water main breaks can close down roads, damage property and lead to expensive repairs. But why do pipes break, and what can you do when it happens? The following can serve as a helpful guide as you seek to be proactive with your infrastructure and educate your customers.
A city’s water distribution system is made up of an interconnected network of pipes. These systems have large transmission lines that feed smaller distribution lines (the ones that lead to residents’ homes). A series of valves throughout a city's system controls pressure and flow. Water towers store the water until it's needed, then gravity brings it into homes and businesses. With so much complexity and so many pipes working to serve our communities, water main breaks can happen anywhere and at any time. Here's a closer look at why.
Why do water mains break?
Water main breaks happen for a number of different reasons. Whether age or accident, pressure changes or corrosive soils, here are a five simple animations that illustrate why breaks happens.
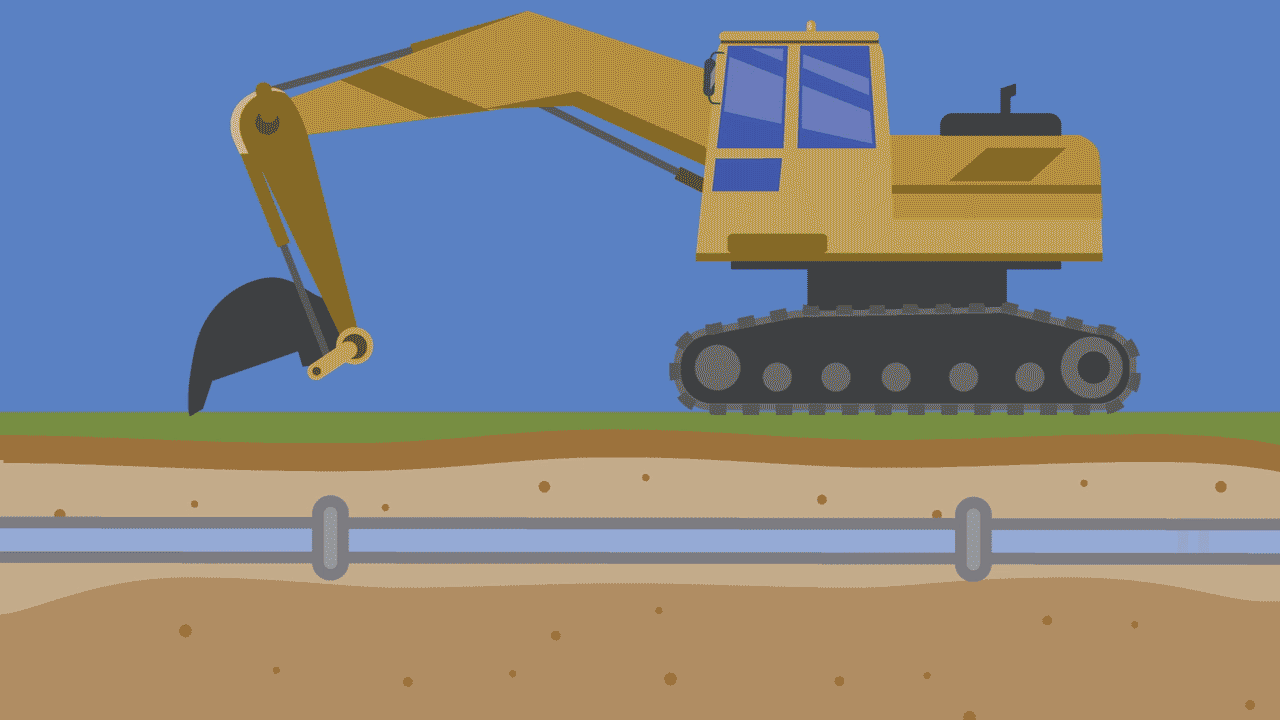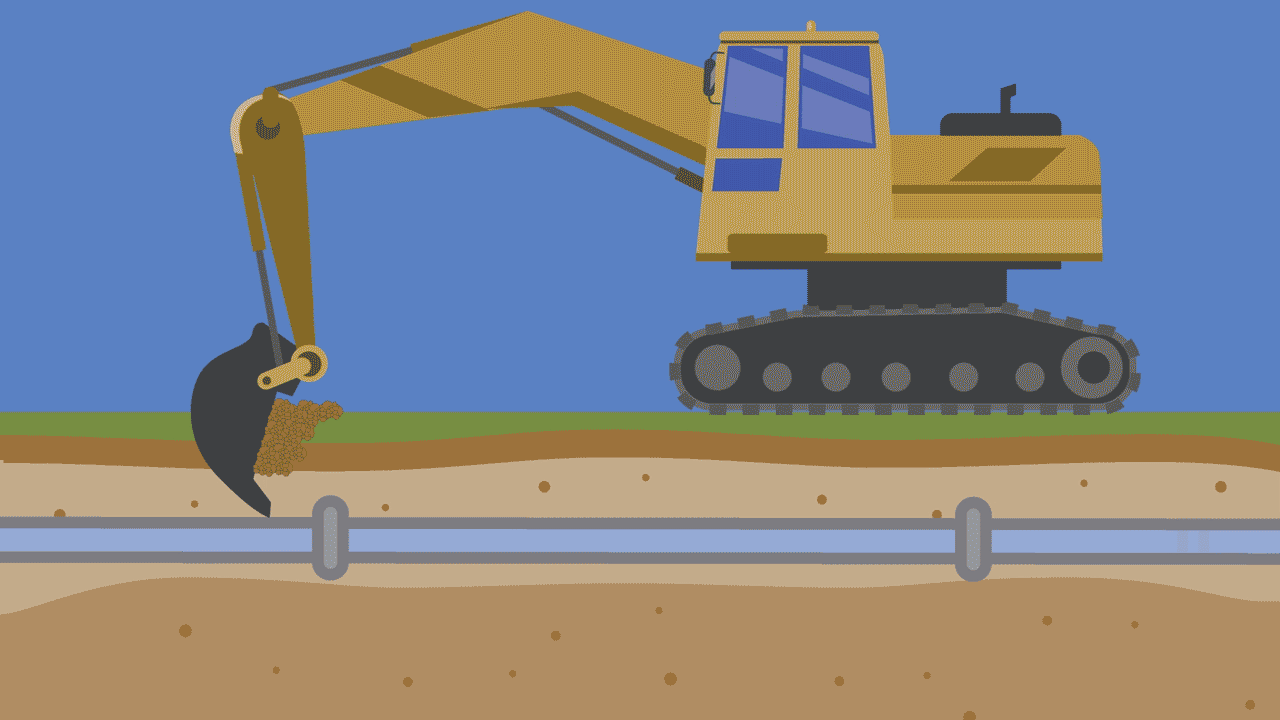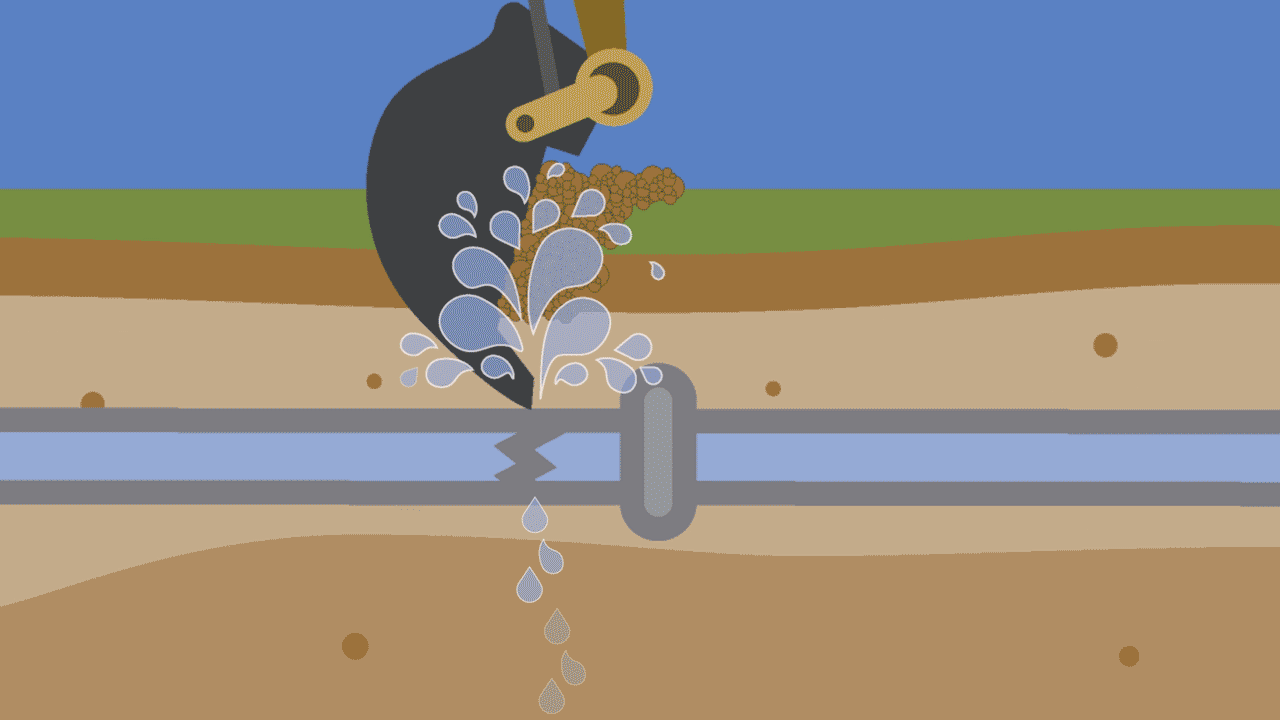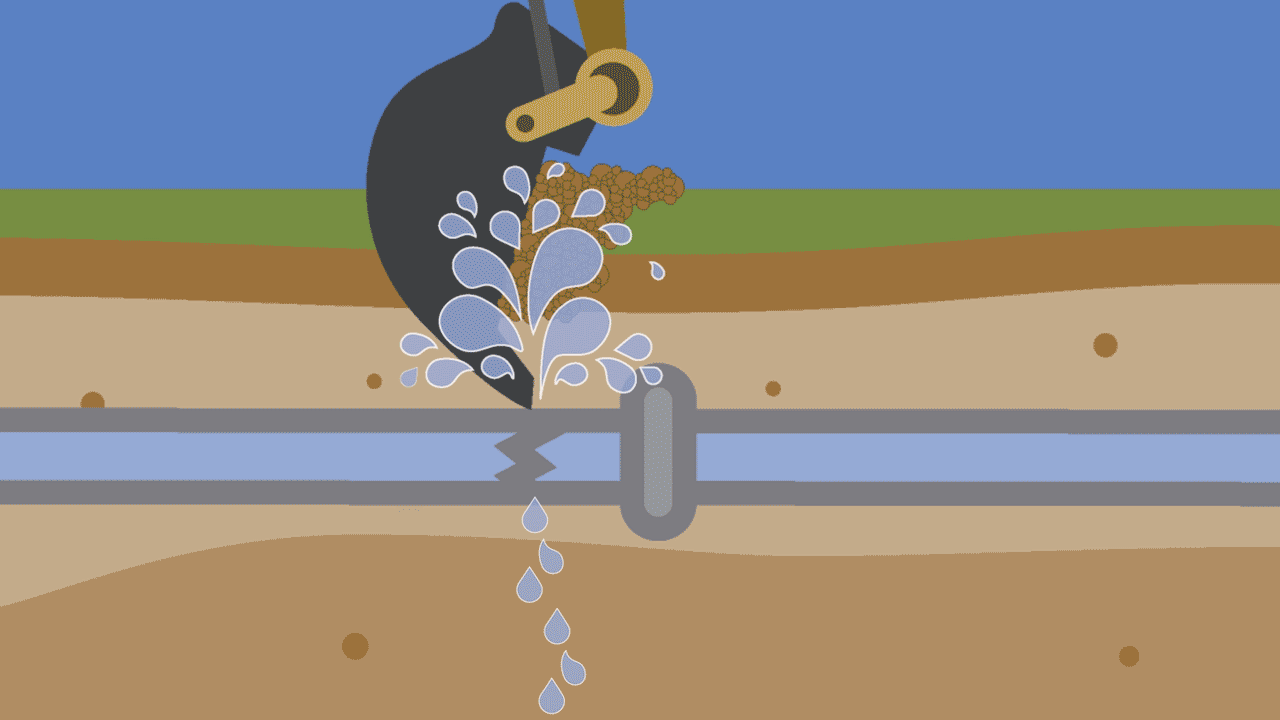
1. Excavation work
When contractors, utility workers or even homeowners dig into the ground, they can unintentionally strike water pipes with their digging equipment. It can happen with a tool as simple as a shovel or, more commonly, with heavy excavation machinery. The need for proactive research and careful construction cannot be overstated.
2. Pipe age and material
Older pipes are more likely to break. For example, water mains installed before 1980 were often made of cast iron. Cast iron can be brittle and doesn't expand and contract easily with temperature changes. When this happens, the pipes have a tendency to crack. There are also older sewer pipes that are made of clay. This material also breaks easily. Water mains today are often made of ductile iron or plastic pipes to proactively avoid issues such as these. If your pipes are decades old, it may be time to examine their status.
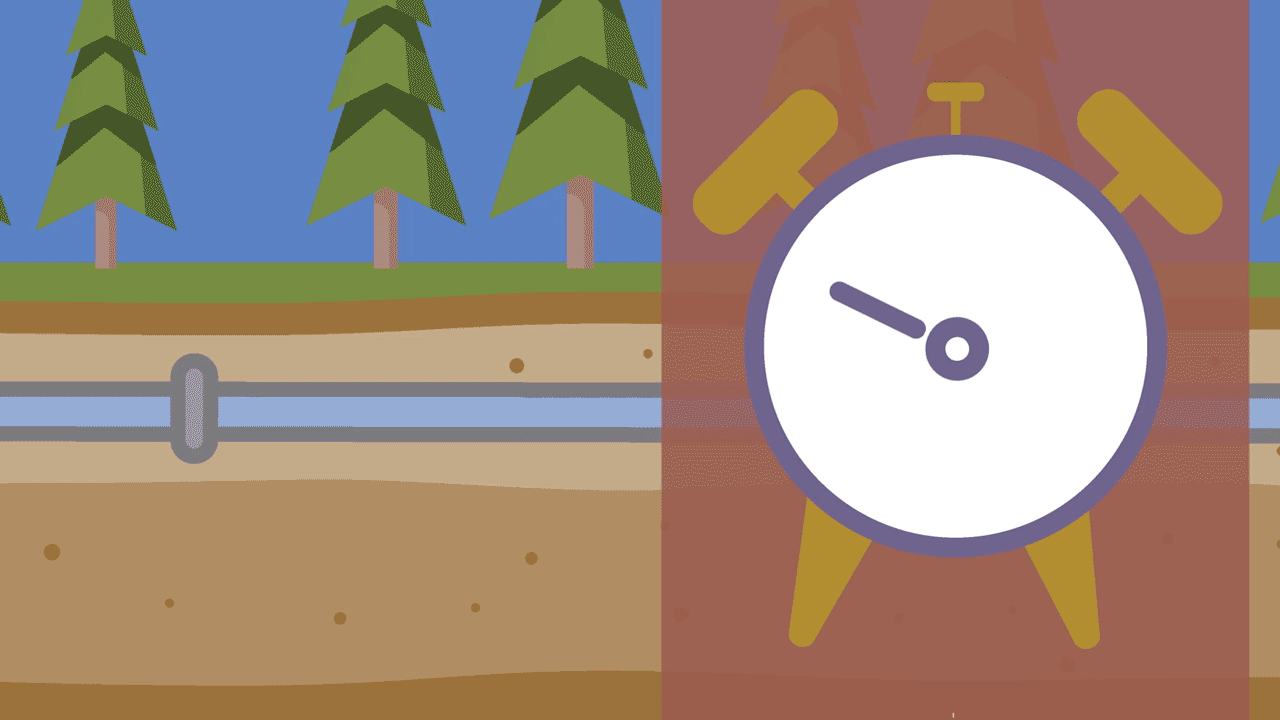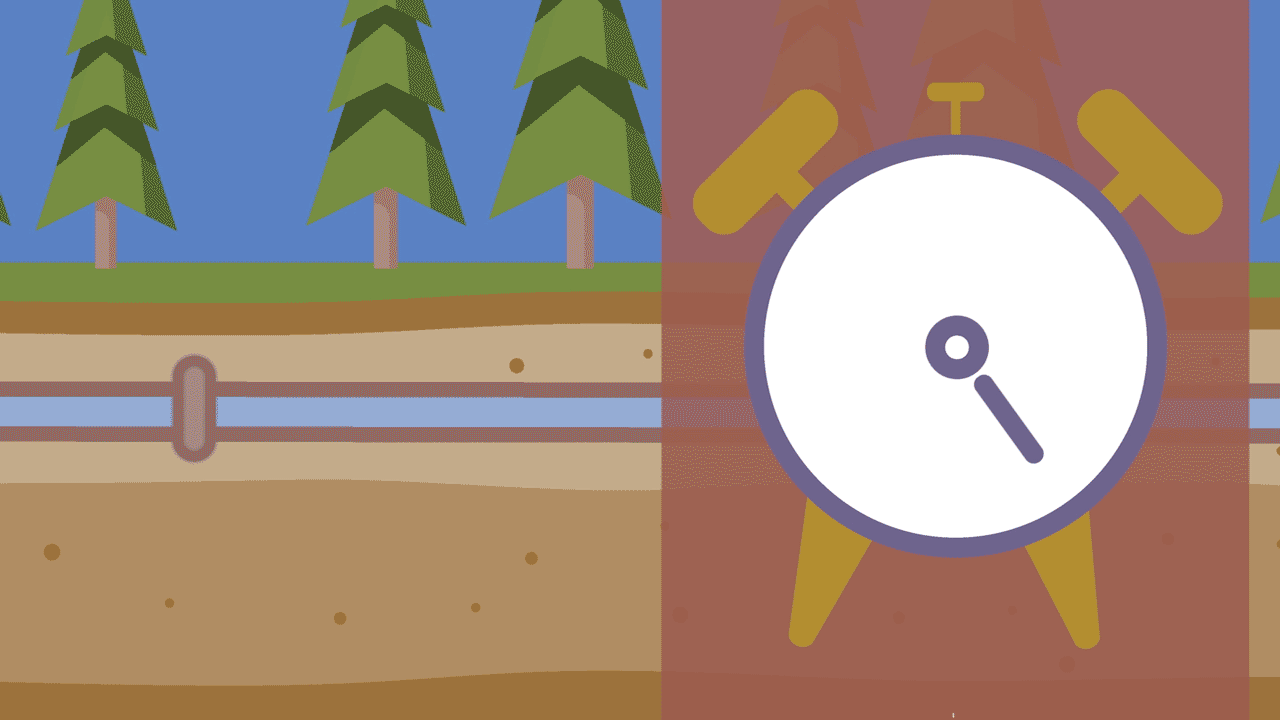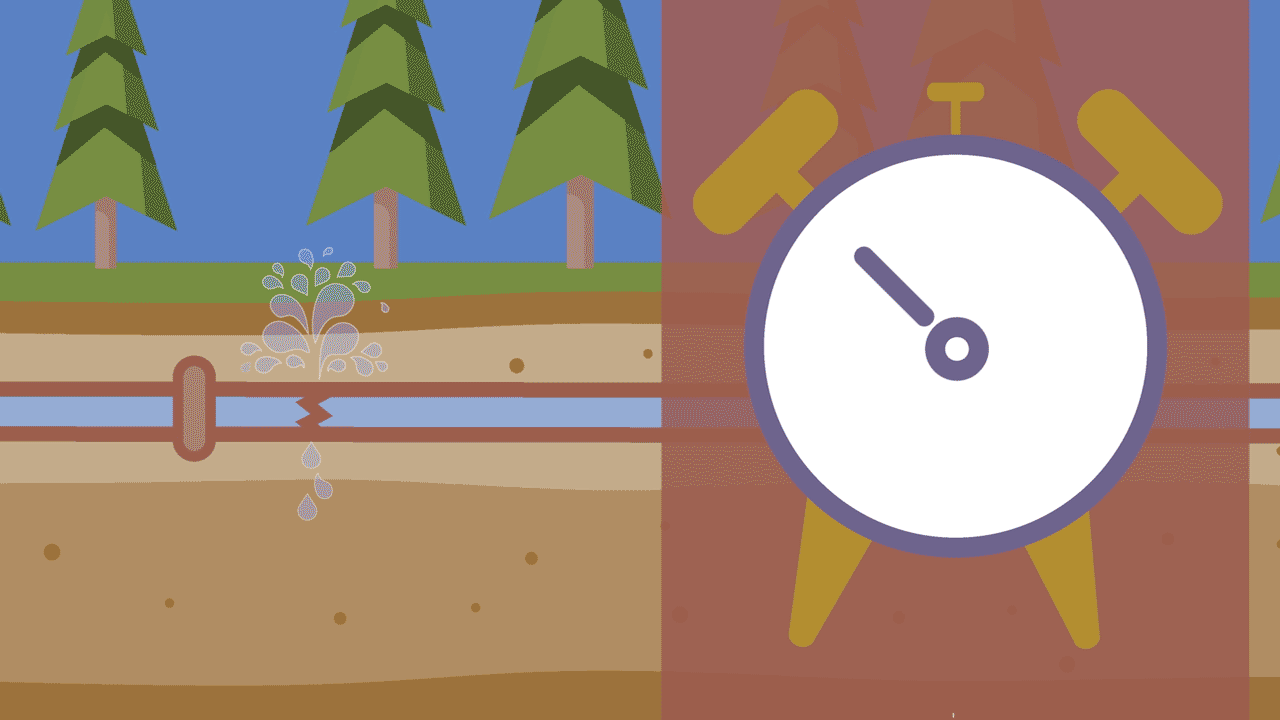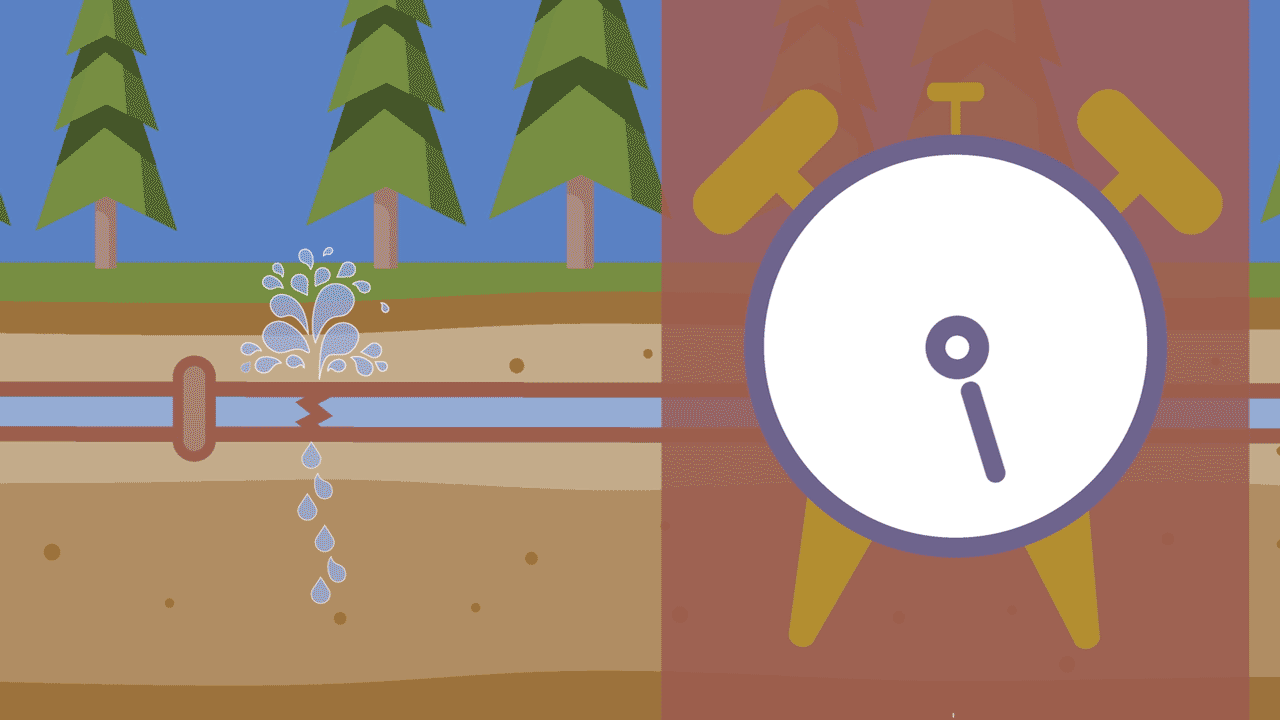
3. Pressure changes
The pressure inside a water main can change in a couple different ways. One of the most common ways is through temperature changes, sometimes called thermal expansion. As the ground around a pipe freezes and heats, the pipes expand and contract – sometimes causing a rupture. Pressure changes can also occur when fire hydrants are either opened or closed too quickly. This is called water hammer.

4. Ground settling
Over time, as the soil around a water main settles it can stress the pipes running beneath the ground. If the ground settles enough, the stress can break the pipe.
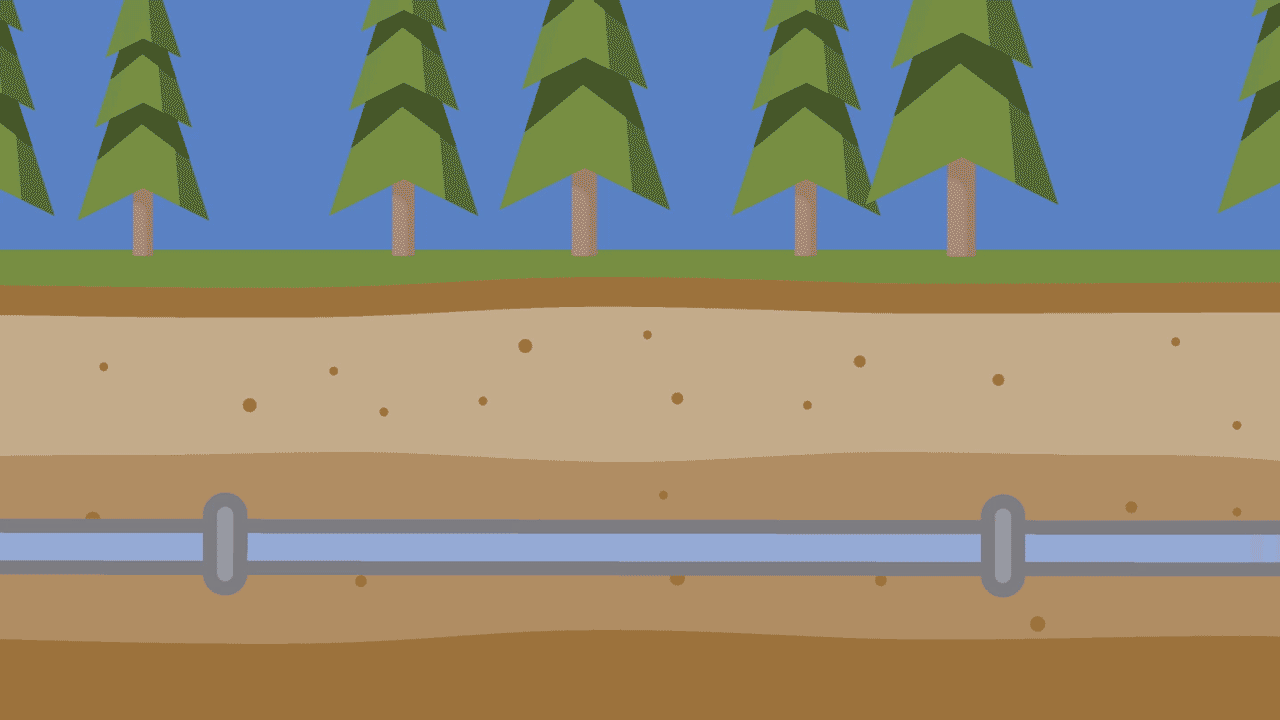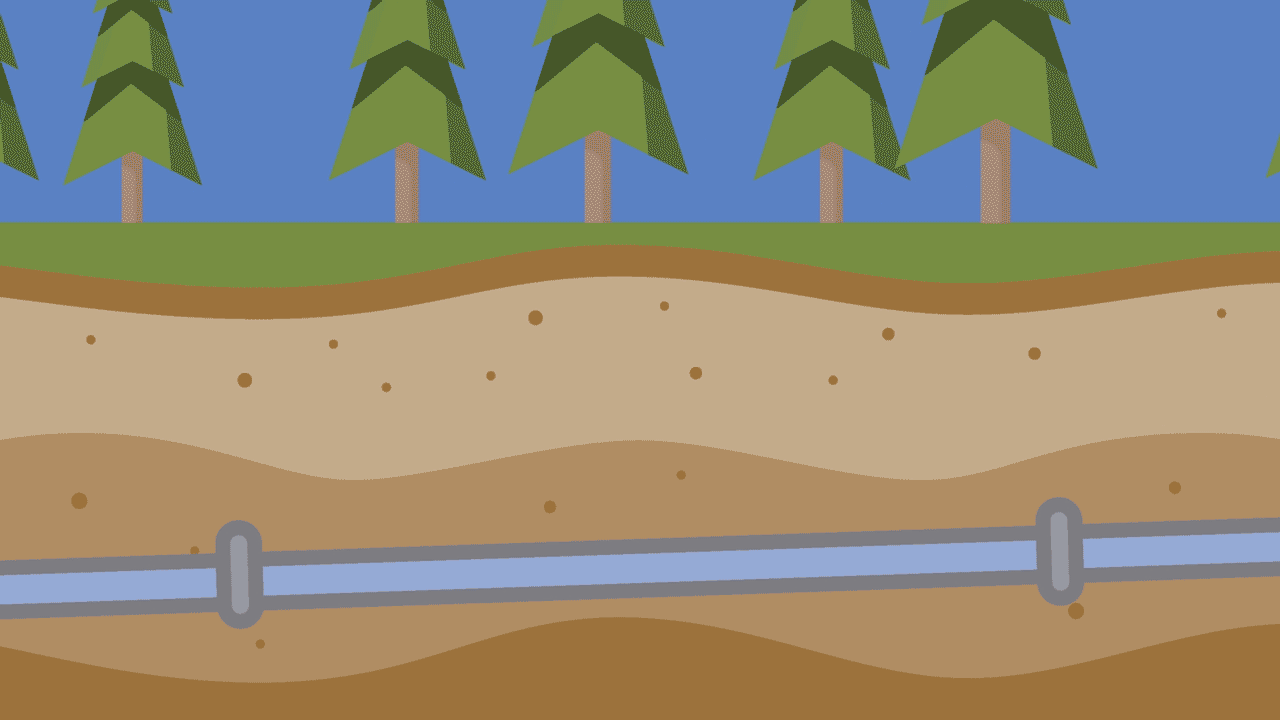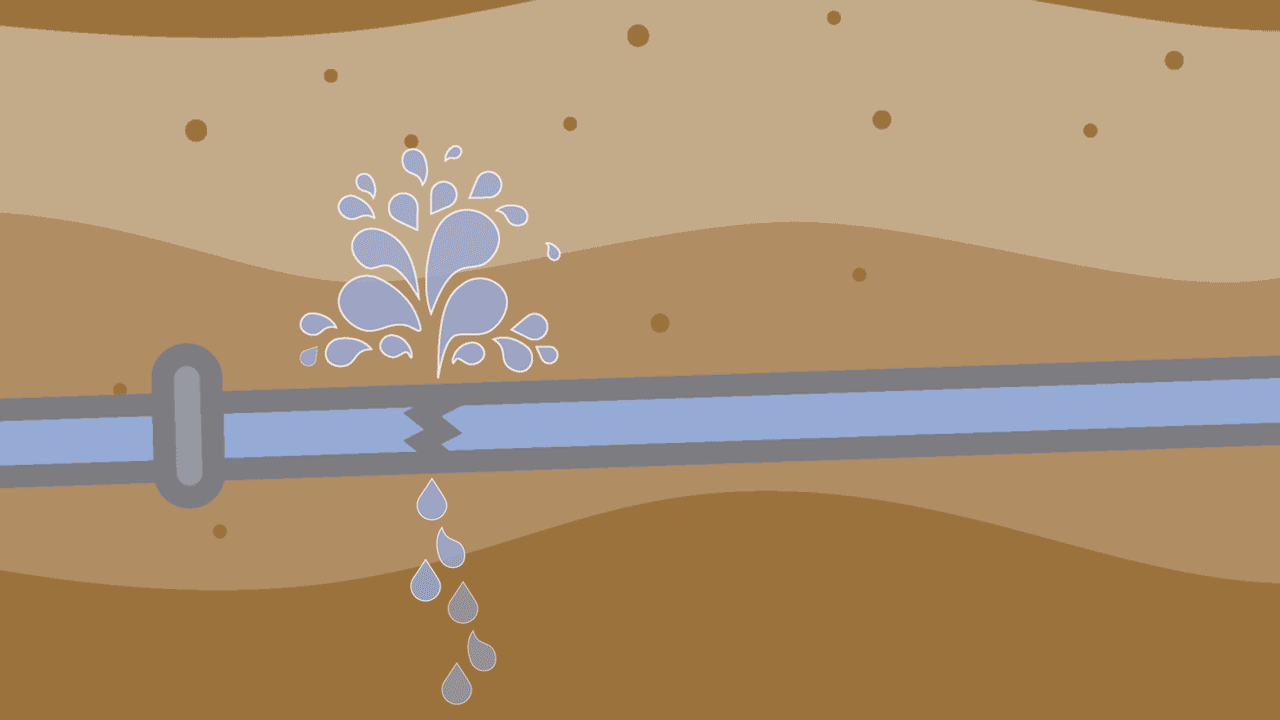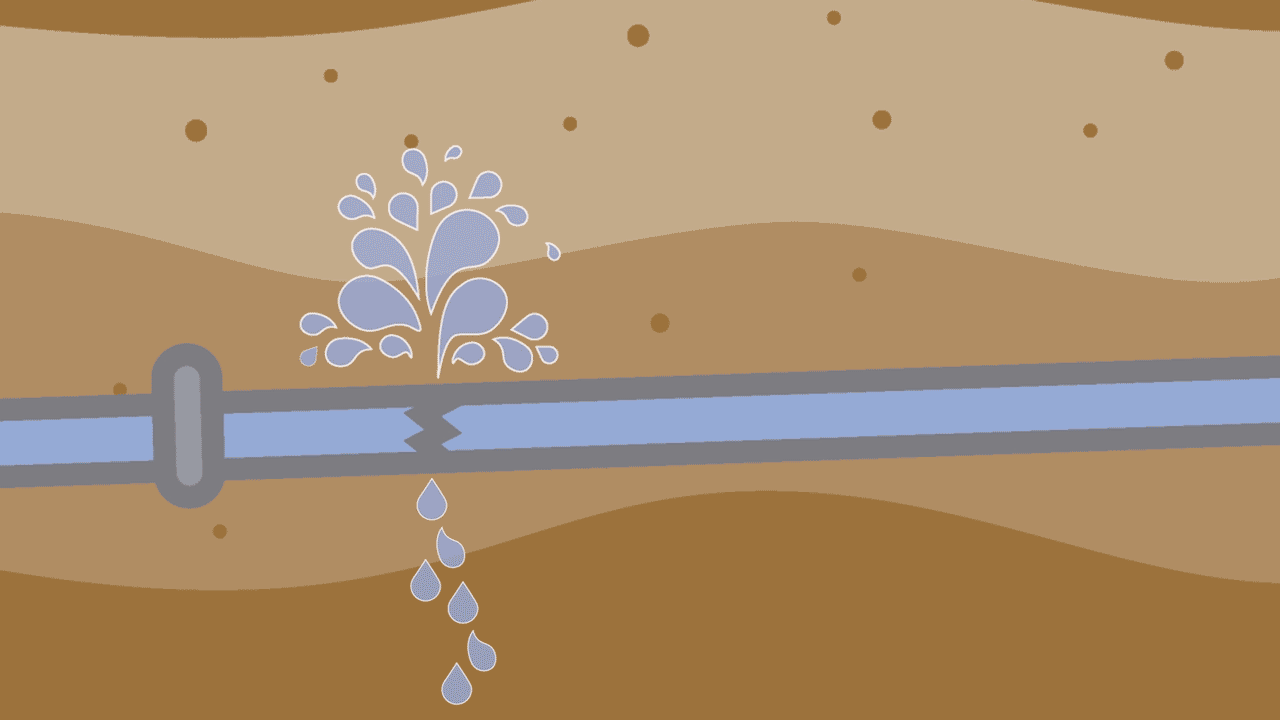
5. Corrosive soils
Some soils are corrosive and can eat away at pipes over time. This is especially common in iron and other metal pipes. Eventually the corrosion causes the pipe to break. It happens most often at pipe fittings or in pipes that haven't been properly protected from corrosion. The Ductile Iron Pipe Research Association (DIPRA) suggests polyethylene encasement as a popular, economic and successful method of corrosion control. Some communities have opted to use pipe made out of non-corrosive materials such as C-900.
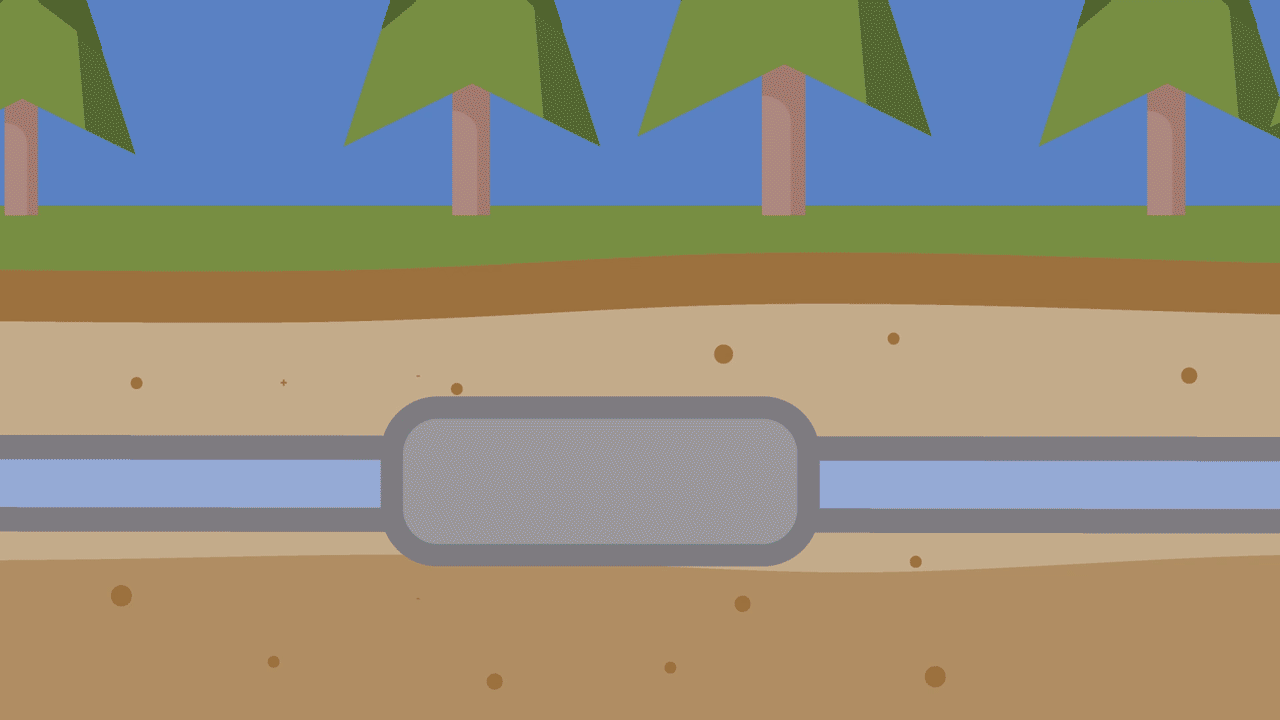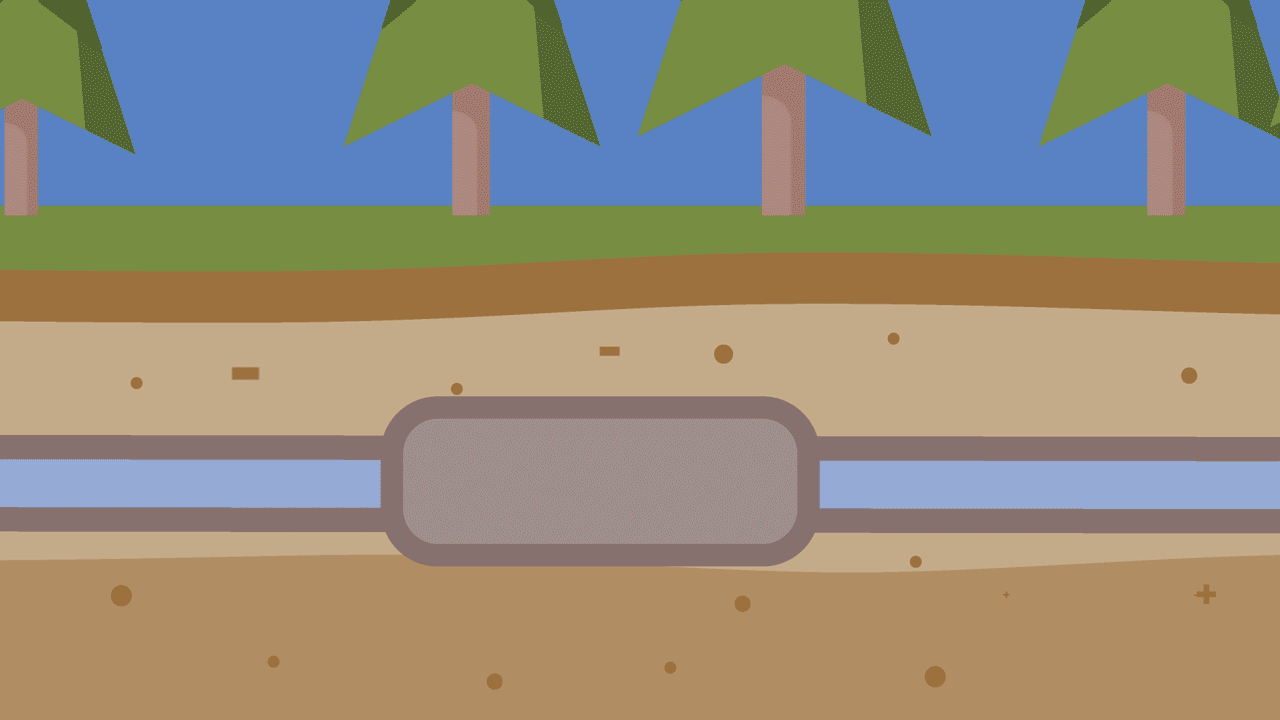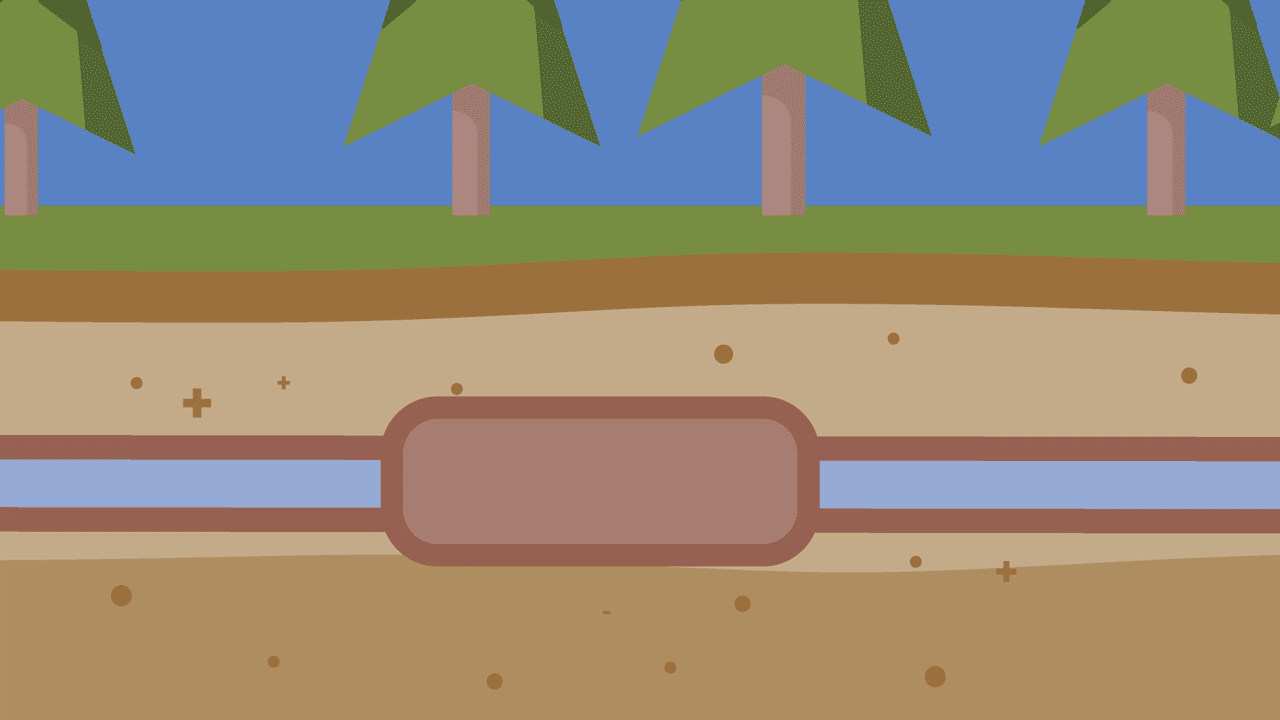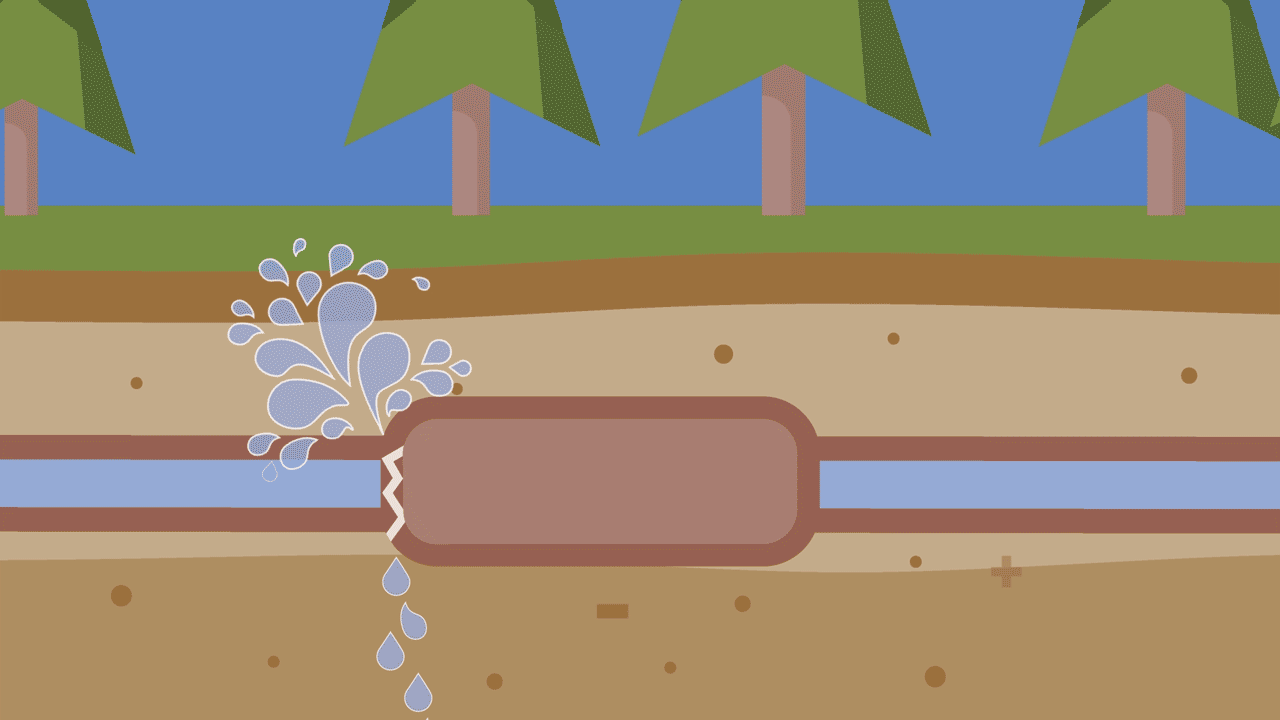
What can you do when pipes break?
There are a number of paths forward when water mains break and cause problems in a community. It's important to choose a consultant that offers a number of diagnostic and repair solutions, because each case is different.
Water main condition surveys help identify issues early on to avoid long-term issues. To assess the condition of water mains, engineers research physical, environmental and operational factors to create a Forces & Issues (F&I) Matrix that identifies the range of potential alternatives for the replacement/rehabilitation of the mains. The F&I Matrix helps identify potential problems, along with replacement/rehabilitation alternatives and their costs to guide rehabilitation priorities for communities.
There are also innovative methods like non-destructive testing and trenchless technology that repair broken pipes without disturbing the ground around it. Be sure to explore the best path forward based on your unique needs, and proactively evaluate the state of your infrastructure. Learn more about possible solutions by downloading our State of Water Infrastructure eBook.
Related Content: The State of Water Infrastructure – Trends, Challenges and How to Be Proactive Amidst Constant Change [eBook]
Bringing it all together
Water main breaks can disrupt communities both immediately and sometimes for the long term. Digging deeper into why breaks happen and what your options when they do, or to prevent breaks, can lay the foundation for reduced costs, most proactive measures, and a fully engaged and educated community.
About the expert

Greg Anderson, PE*, is a civil engineering leader and senior project manager who specializes in municipal engineering. With more than 25 years in the industry, Greg understands the importance of educating communities on how their infrastructure works and providing solutions when improvements are needed.
*Registered Professional Engineer in MN

.png?width=113&name=SEH_Logo_RGB%20(1).png)
